│By Clem Delany, Associate Acquisitions Editor, Gale Primary Sources│
The twentieth century was an era of global conflict and careful diplomacy, of the rise and fall of political extremes, of great strides in technology and vast change in the everyday lives of people around the world. Britain began the century with an empire that straddled the globe, and ended it with just a handful of small overseas territories. Warfare moved from trenches and bayonets, to weapons of mass destruction and long-distance drones. The global population skyrocketed. The internet came to be.
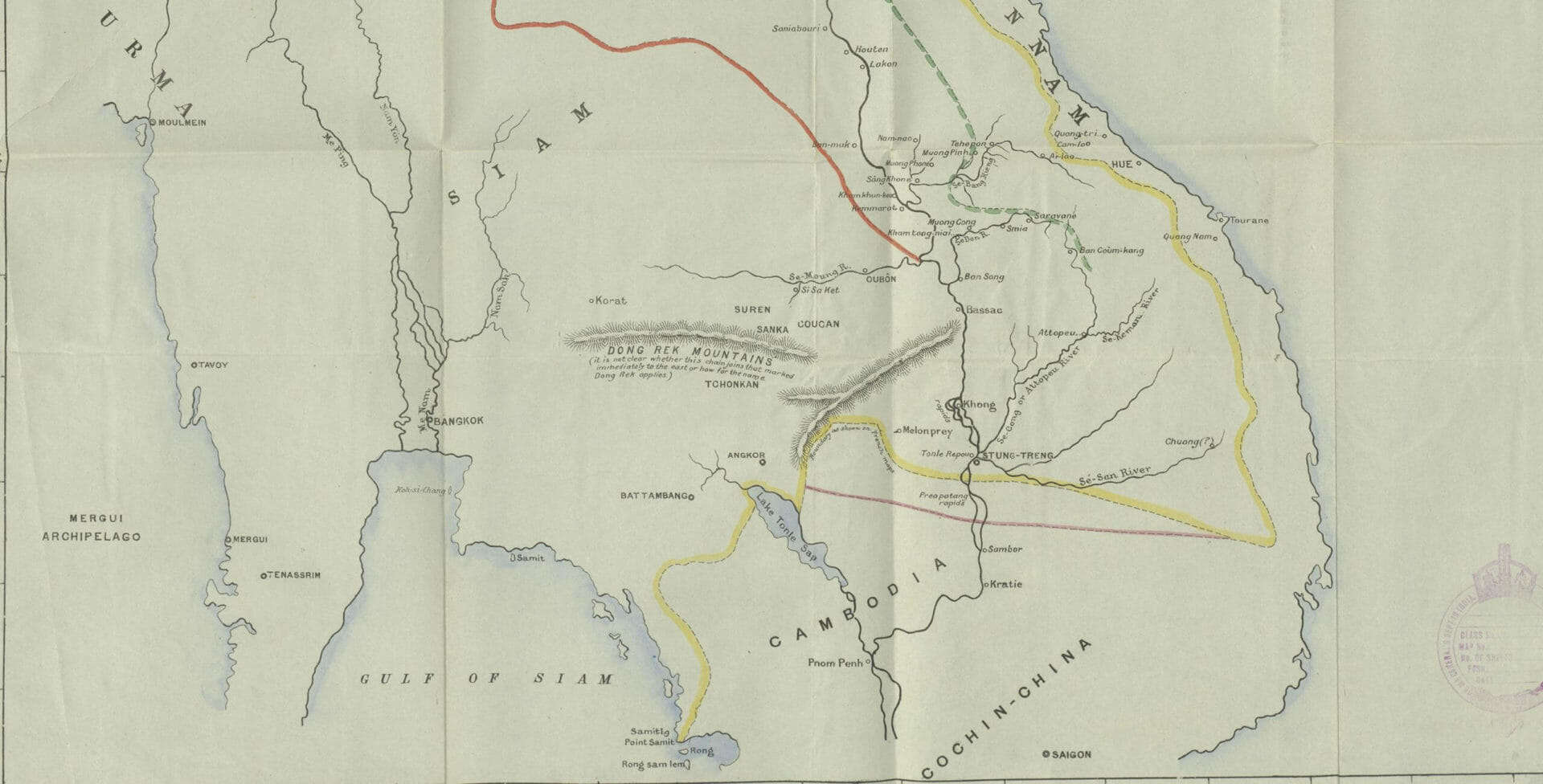
The scope and geographical spread of the interests of the British government over this century was vast. It reached beyond the UK and the mandates, protectorates and colonies of the British Empire, to the affairs of the self-governing Dominions and the later Commonwealth, as well as those of allies and enemies. British interests and British intelligence reached every corner of the globe from Aden to Zanzibar.
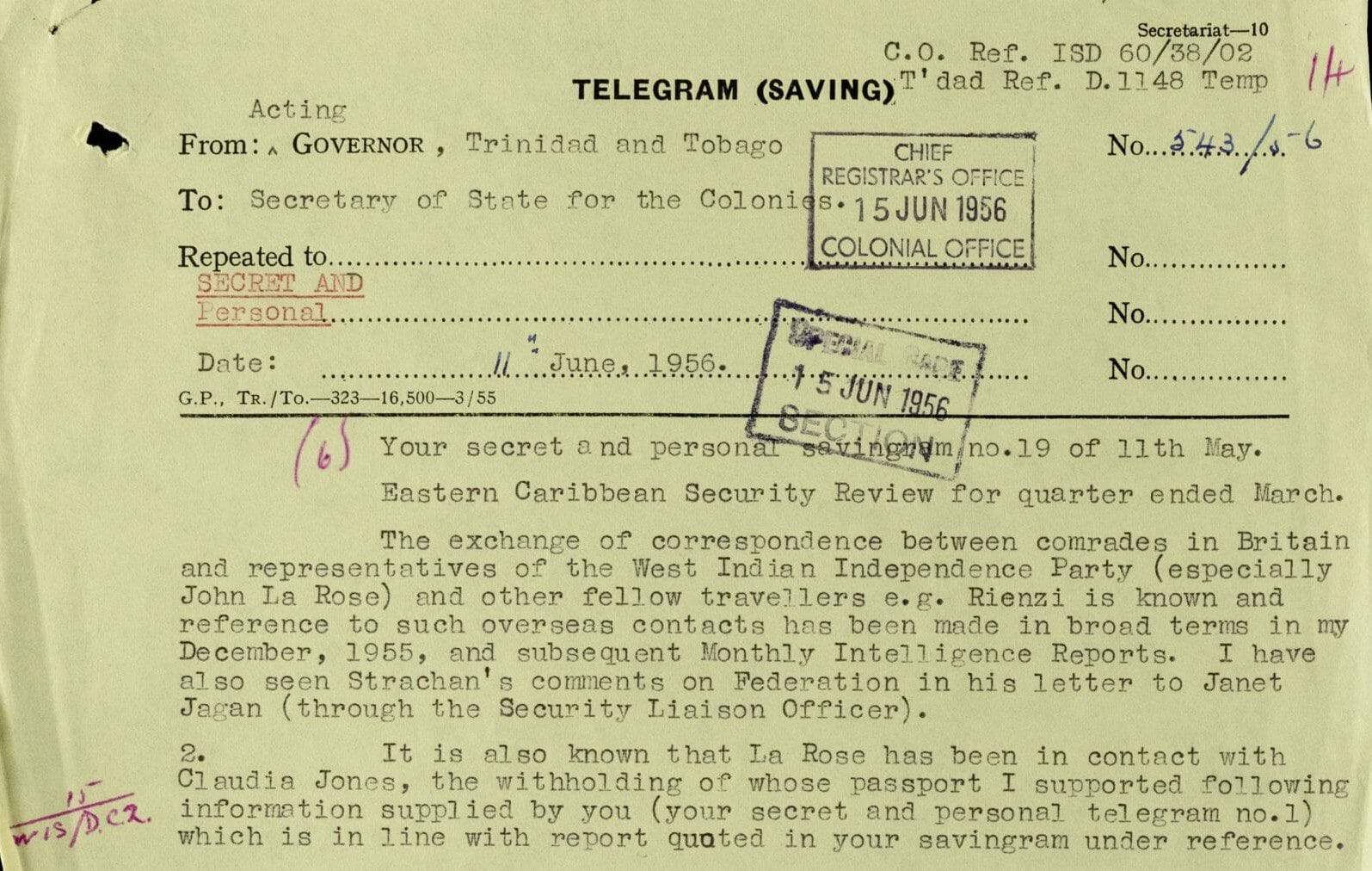
Declassified Documents Online: Twentieth-Century British Intelligence, An Intelligence Empire makes available online over half a million pages of British government papers relating to security and intelligence work in the twentieth century. It brings together files from the Security Service (MI5), the wartime Special Operations Executive (SOE) and Ministry of Economic Warfare, the Intelligence and Security Departments of the Colonial Office in the twilight of Empire, communications and intelligence records of the Ministry of Defence, and material from the Cabinet Office, including Joint Intelligence Committee reports, documents from the Special Secret Information Centre of WWII, and papers of the Cabinet Secretary relating to intelligence and espionage matters.
Read more