│By Sofía Sanabria de Felipe, Gale Ambassador at the University of Oxford│
With great power comes great responsibility. With being a doctoral researcher comes the ever-present question: what do you work on? As a response, you come up with an elevator pitch that somewhat does justice to your project. To do so, you find yourself using abstract terms like ‘universality’ and ‘contingency’, often leaving your audience none the wiser as to what exactly it is you do.
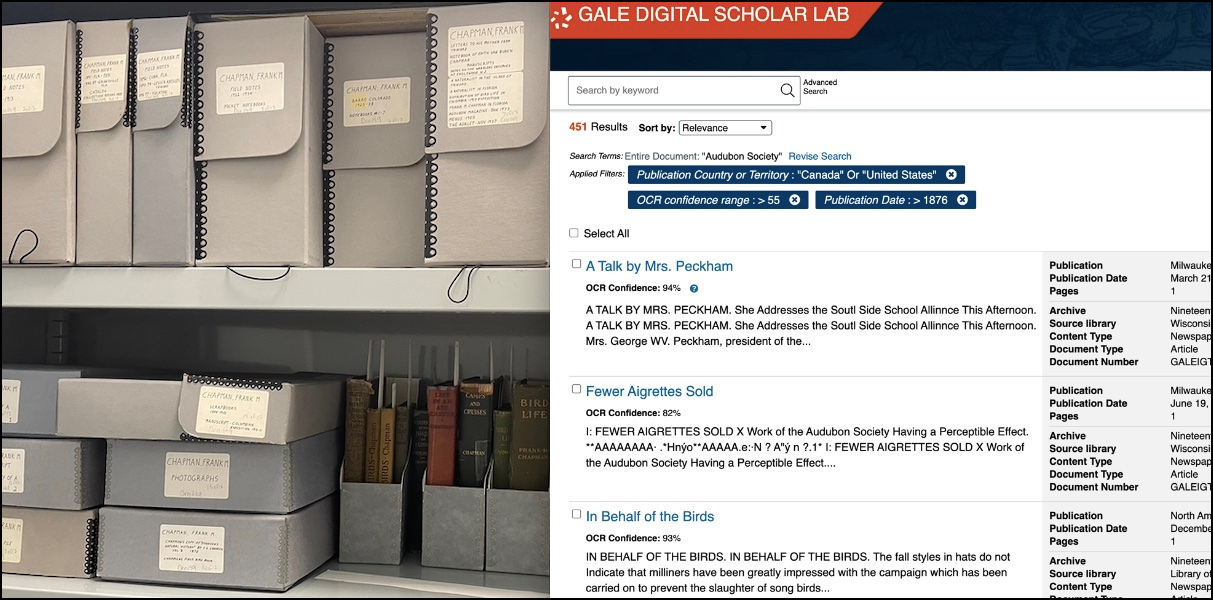
So, when Gale Primary Sources offered me the opportunity to write a blog post centred on my research, I decided to use their archives and digital humanities tools as a way of finally perfecting my elevator pitch.