Learn more about China and the Modern World: Imperial China and the West Part II, 1865–1905 in this blog post – or register below for a live webinar!
|By Liping Yang, Publishing Manager, Digital Archive and eReference, Gale Asia|
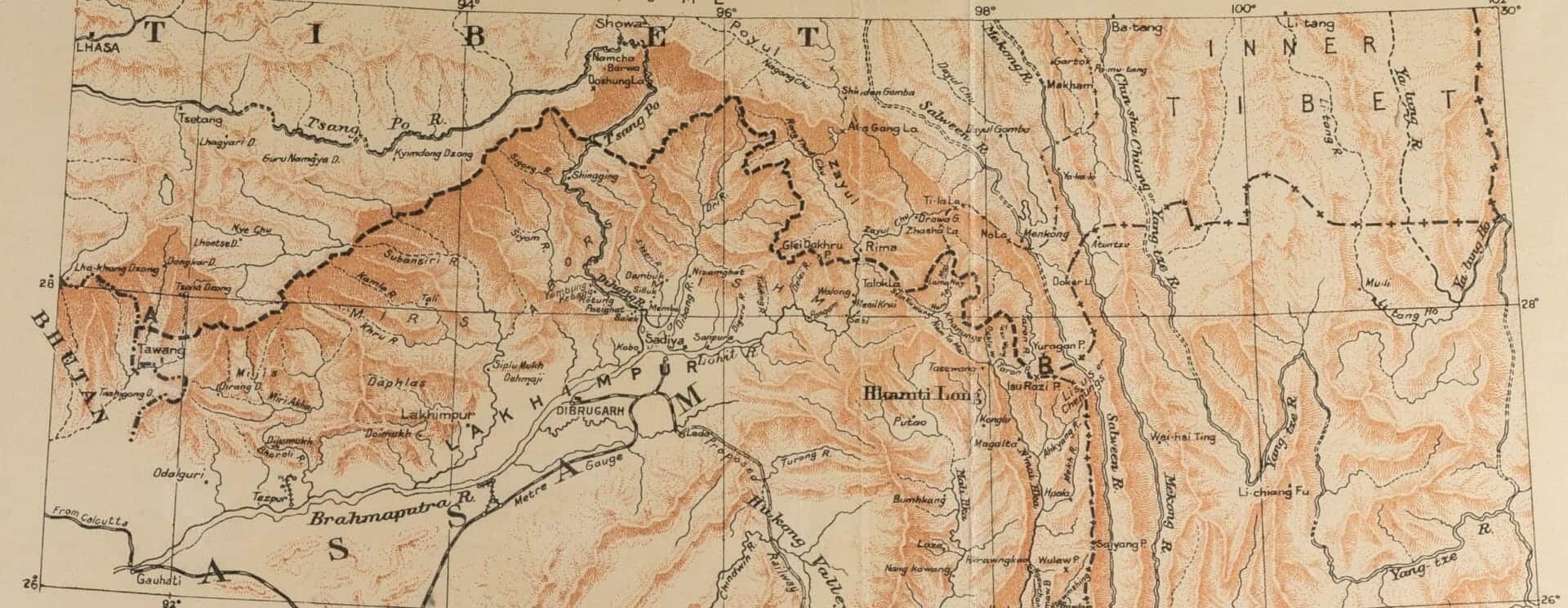
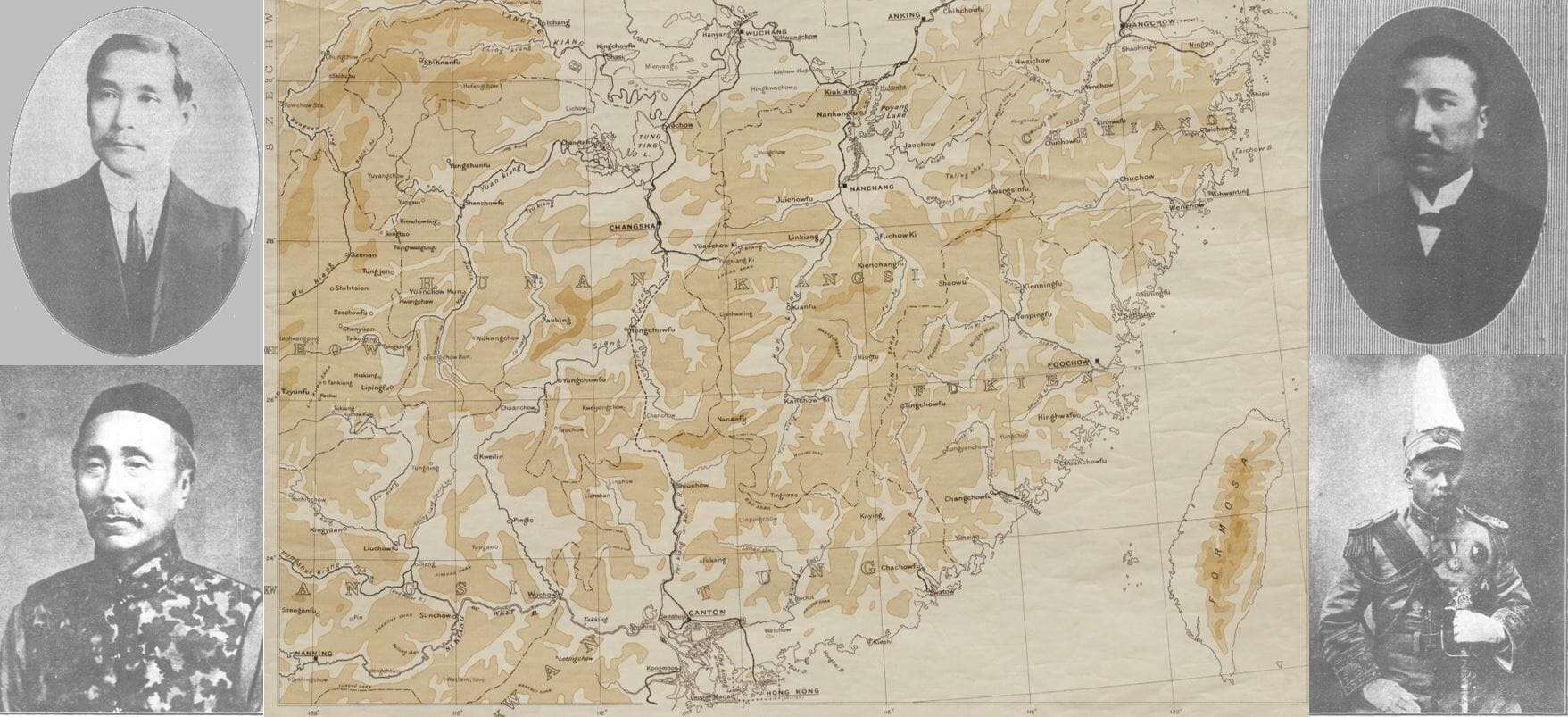
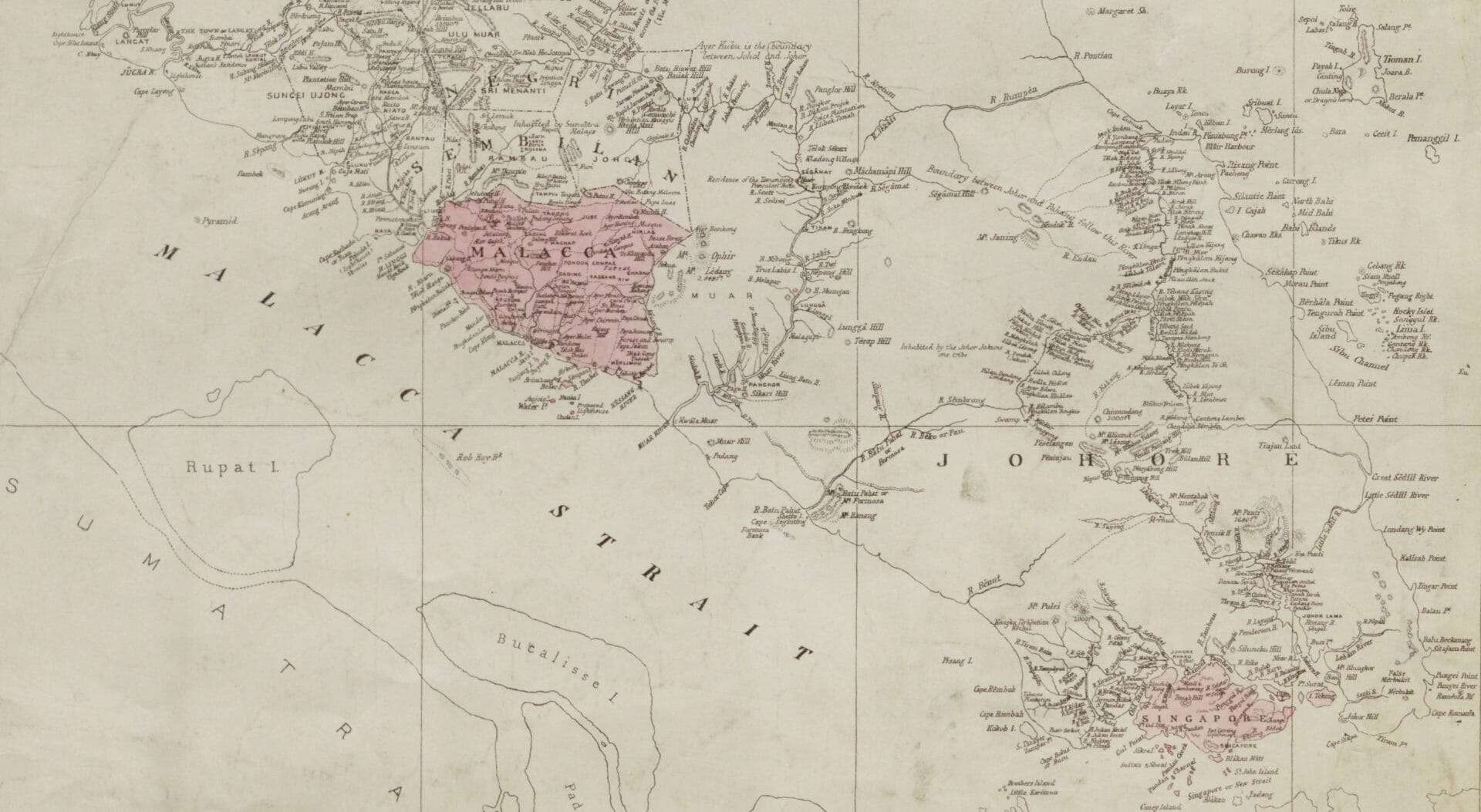
Gale has recently released China and the Modern World: Imperial China and the West Part II, 1865–1905. Consisting of volumes 873–1768 in the highly acclaimed FO 17 series of British foreign office files plus seven volumes of Law Officers’ reports relating to China from FO 83, Part II covers the latter half of the nineteenth century (see my first blog post about this module – Rediscovering China and the World in the Nineteenth Century for the main topics covered in Part I). The complete Imperial China and the West provides a vast and significant primary source archive for researching every aspect of Chinese-Western relations from 1815 to 1905.
Here, with the help of Handwritten Text Recognition (HTR) technology, researchers will be able to conduct full-text searches across more than one million pages of manuscripts relating to the internal politics of China and Britain, their relationship, and the relationships among Britain and other Western powers—keen to benefit from the growing trading ports of the Far East—and China’s neighbours in East Asia, South Asia, and Southeast Asia. Imperial China covers a wide range of topics including diplomacy and war, trade, piracy, riots and rebellions, treaty ports, Chinese emigration, and railway building. In this blog post I’ll walk you through some of the fascinating topics and themes covered in the approximately 600,000 pages of manuscripts included in Part II.
Read more