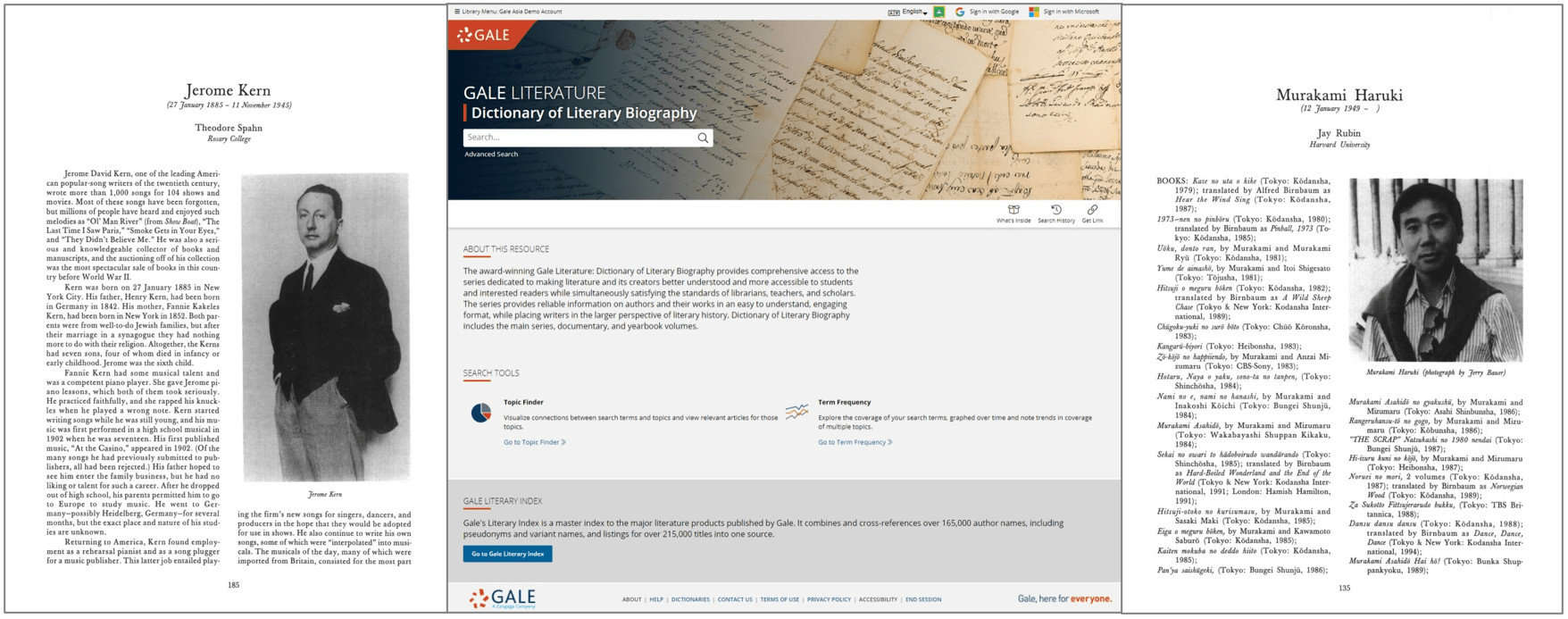
|By Masaki Morisawa, Senior Product Manager, Library Reference, Tokyo|
If you watched the recent Olympics, you’ll know that August in Tokyo is brutally hot and humid. This was more or less true two and a half decades ago when I was an English Literature student. Cash strapped, with nothing better to do, I would often spend my August days in the air-conditioned university library, just to avoid the intolerable heat! My favourite place was the reference area where they had rows and rows of Gale Literature volumes (I’m not making this up). There were literally hundreds of volumes stacked in those rows, from the rainbow-coloured Contemporary Authors volumes, to the brown buckram Literature Criticism volumes; but my personal favourite were the light-blue Dictionary of Literary Biography volumes. I would often pull out several of those DLB volumes and browse through the entries while I passed time in my favourite corner seat by the windows.