│By Sarah L. Ketchley, Senior Digital Humanities Specialist│
In today’s rapidly evolving academic landscape, digital tools are reshaping the way we study literature, history, and culture. As digital humanities (DH) becomes increasingly central to research and teaching, instructors—particularly graduate students and early-career faculty—often find themselves faced with the challenge of integrating digital methodologies into their courses. To address this need ‘Introduction to Digital Humanities‘ offers a structured, assignable course designed to equip students with essential digital research skills. It provides an accessible, hands-on approach to digital humanities, helping instructors save valuable time while fostering critical data literacy in students.
‘Introduction to Digital Humanities‘
Computational methods are now integral to humanities research. However, many students enter university with little exposure to data-driven scholarship. ‘Introduction to Digital Humanities‘ bridges this gap by offering a clear, engaging introduction to the field.
Built around Gale Primary Sources and Gale Digital Scholar Lab, this course provides structured guidance on fundamental DH methods. Whether implemented as a full course or selectively integrated into existing curricula, ‘Introduction to Digital Humanities’ offers a grounding in approaches to digital scholarship using primary source archives, while demystifying complex digital methodologies – making them accessible to students at all levels.
Who is the Course For?
‘Introduction to Digital Humanities’ is designed for a range of educators and researchers, including:
- Graduate students and early-career instructors seeking structured materials for teaching DH for the first time.
- Faculty in humanities disciplines looking to integrate computational methods into their teaching.
- Librarians and archivists aiming to support digital research literacy among students.
- Researchers and educators interested in incorporating text mining and data analysis into humanities education.
The course is flexible and designed to be adapted according to the instructor’s requirements. Individual modules can be taught as standalone workshops, or the course can be offered over a quarter or semester, while the skills learned can be used in all humanities disciplines.
Course Structure: Six Key Modules
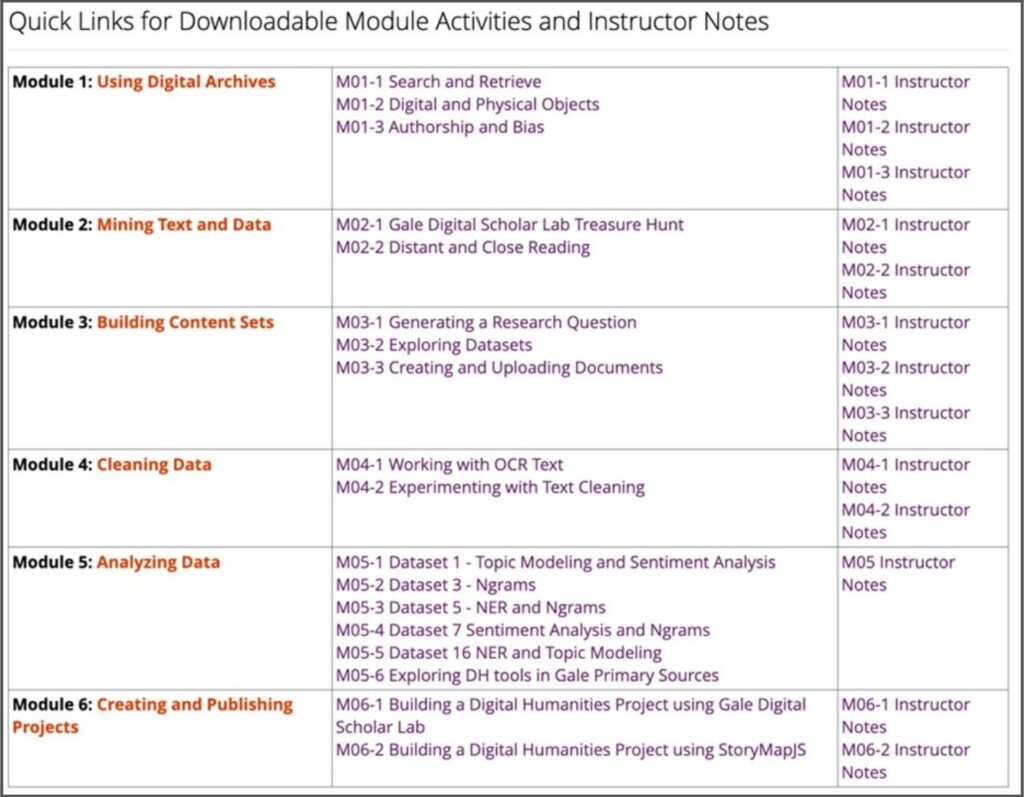
The course is organised into six modules, each covering a fundamental aspect of digital humanities research:
- Using Digital Archives – Students explore digital archives, learning about how primary sources are collected, curated, and accessed online.
- Mining Text and Data – This module introduces computational text analysis, showing how scholars uncover patterns and trends in vast textual collections.
- Building Content Sets – Students create their own digital corpora, selecting and organising primary sources for research.
- Cleaning Data – Data preparation is crucial for digital research. This module teaches students how to structure and refine textual datasets.
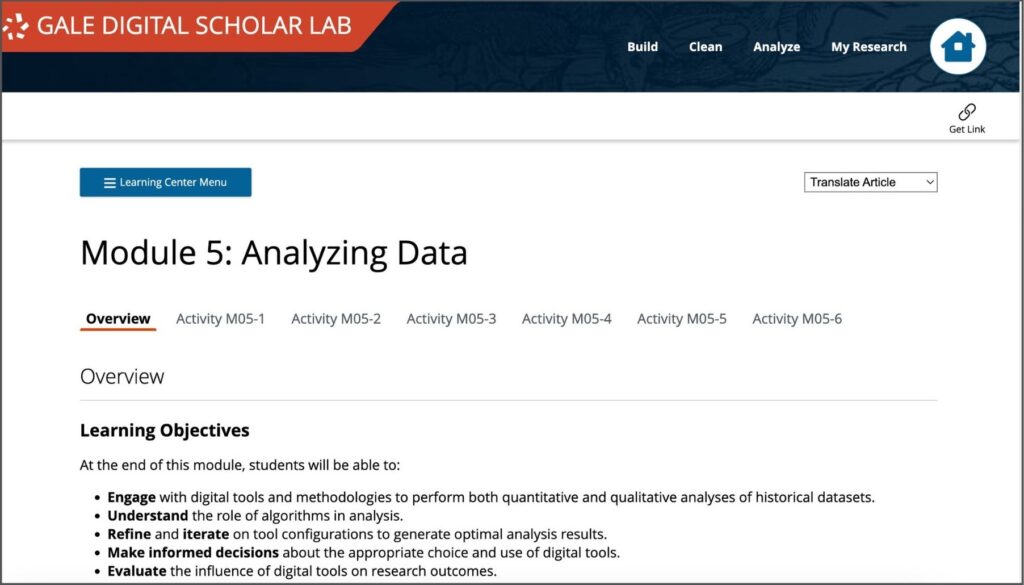
- Analysing Data – Students apply computational techniques to analyse their curated texts, learning how to interpret and critically assess results.
- Creating and Publishing Projects – The final module guides students in developing and sharing their digital humanities projects.
Each module includes relevant readings, discussion questions, hands-on activities, and extended learning opportunities, ensuring that students engage deeply with both theoretical and practical aspects of DH research. All the activities and instructor notes are accessible on the course pages, or as downloadable PDFs. This flexibility allows instructors to adapt the material to suit their individual classroom needs.
Support for Instructors
For instructors who are new to digital humanities pedagogy, ‘Introduction to Digital Humanities’ includes instructor notes for each activity, offering guidance on how to prepare to teach each of the modules.
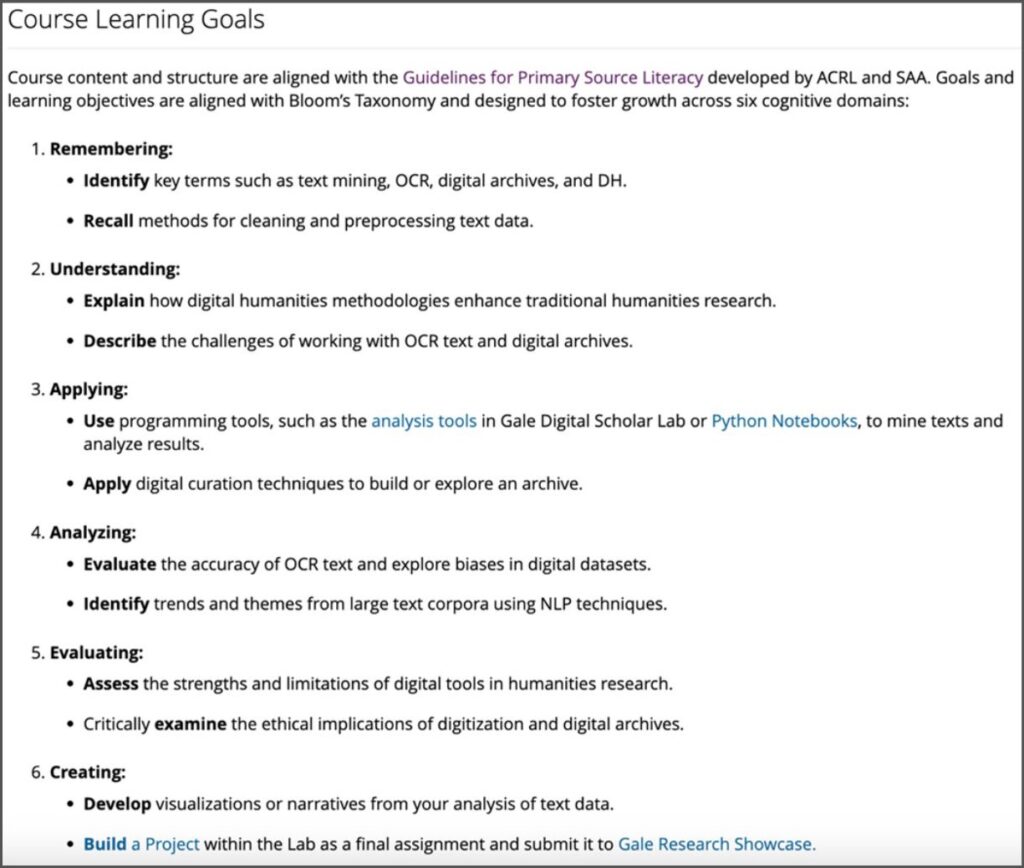
The course aligns with the Guidelines for Primary Source Literacy developed by the Association of College & Research Libraries (ACRL) and the Society of American Archivists (SAA), ensuring students gain essential archival research skills. Additionally, learning objectives are structured around Bloom’s Taxonomy, fostering cognitive development across six domains: remembering, understanding, applying, analysing, evaluating, and creating.
For instructors, the structure and content of the course offers several key advantages:
- Timesaving, assignable content – Ready-made materials allow educators to focus on student engagement rather than curriculum design.
- Flexible implementation – Instructors can use the full course or select specific modules to complement existing courses.
- Support for new digital humanities instructors – The instructor notes provides step-by-step guidance, reducing the learning curve for those unfamiliar with DH pedagogy.
- Alignment with best practices in digital literacy and archival research – The course meets established academic standards, ensuring students receive high-quality instruction.
Learning Outcomes: What Students Will Gain
By completing the course, students will develop skills that are in demand across the career spectrum. They will:
- Gain proficiency in text mining tools and methods, by analysing primary sources and extracting meaningful insights.
- Understand the theoretical and practical foundations of digital archives, by exploring how digital collections are curated and structured.
- Critically analyse computational research results, by developing the ability to assess the strengths and limitations of digital methodologies.
- Create and manage digital text corpora (content sets), by working hands-on and developing their own datasets for research.
- Develop well-documented text-mining projects, by applying course concepts to design and execute their own DH research projects.
- Enhance digital literacy and think critically about data and technology. This course fosters reflection on the ethical and social implications of digital scholarship.
Empowering Instructors and Students in Digital Humanities
The launch of ‘Introduction to Digital Humanities‘ marks an exciting development in digital humanities education. By providing structured, flexible, and pedagogically sound materials, this course ensures that students acquire essential digital literacy skills for the evolving landscape of humanities research. The course offers the resources and support needed to make digital scholarship accessible, engaging, and impactful.
If you have questions about how on how to use the course in your teaching and learning, please get in touch! Email us at [email protected].
If you enjoyed reading about the ‘Introduction to Digital Humanities’ course, check out these posts:
- A Classroom Compendium: Digital Humanities Resources for a New School Year
- Re-imagining Assignments in the DH Classroom: StoryMaps
- Hacking History with Gale Digital Scholar Lab
- Exploring Sentiment in Historical Texts With Gale Digital Scholar Lab’s New “Sentiment by Timeframe” Visualisation
- A Two-Way Relationship – Collaborating with Scholars in the Gale Fellowship Program