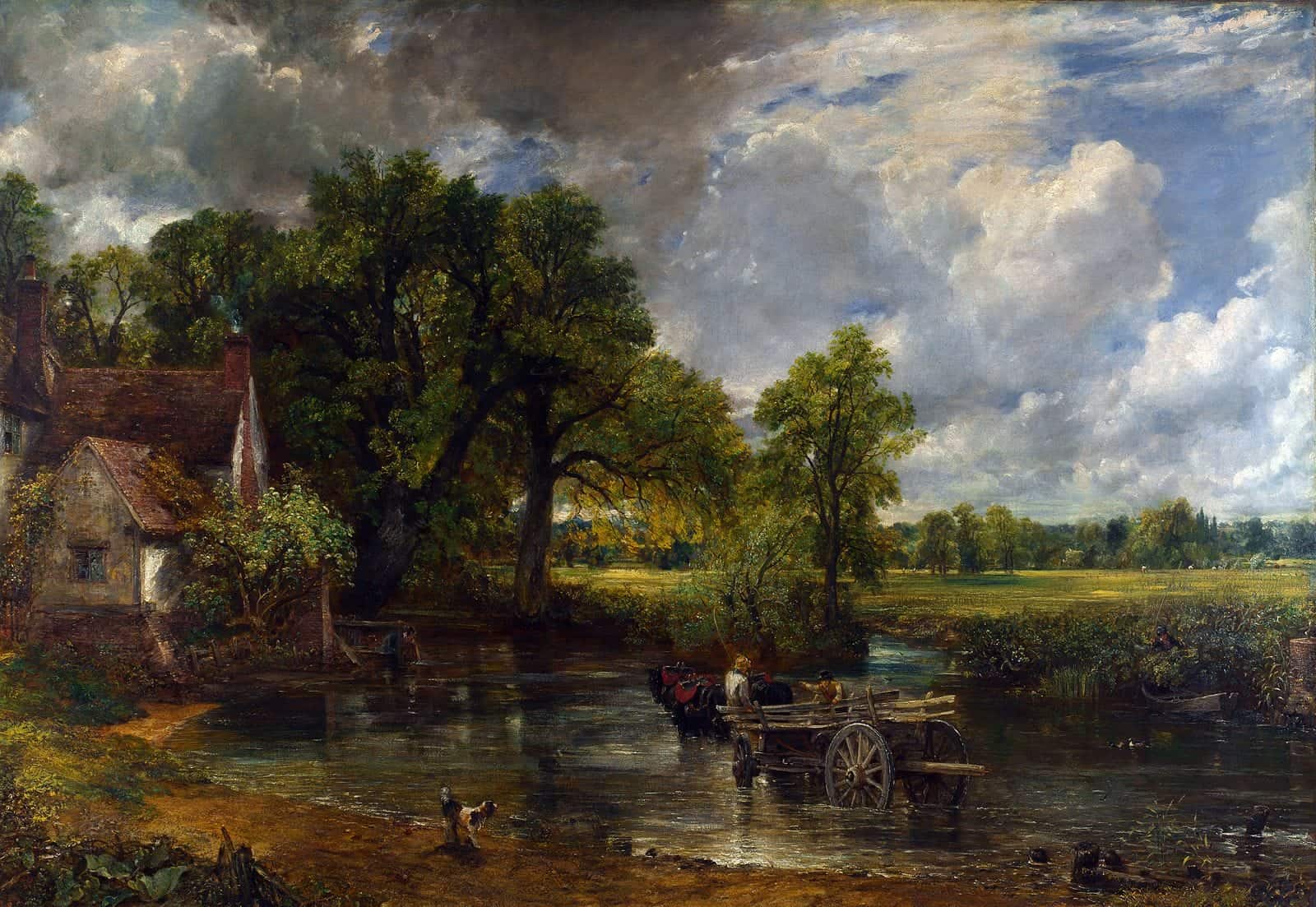│By Isabelle Partridge, Gale Ambassador at the University of Exeter│
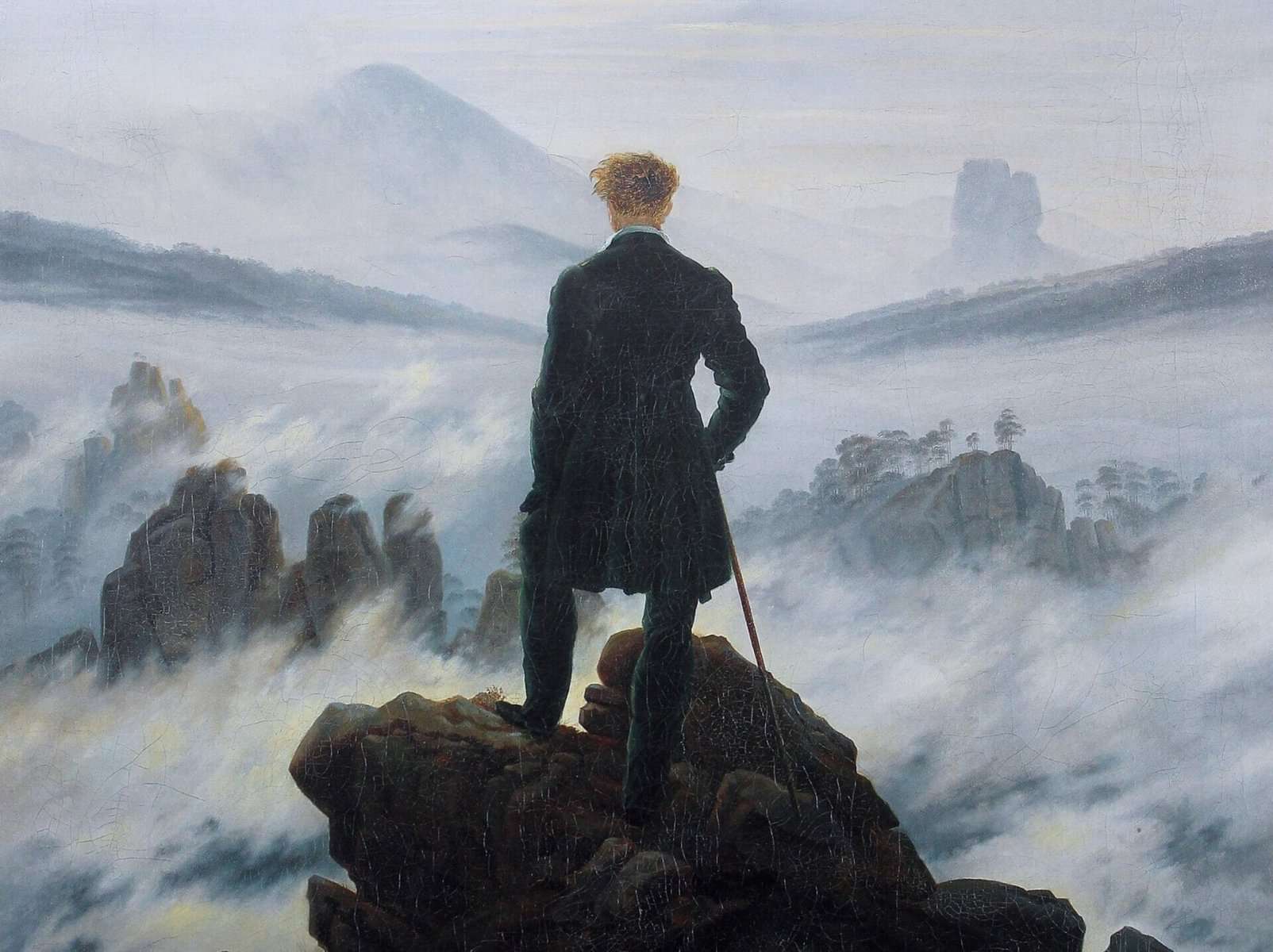
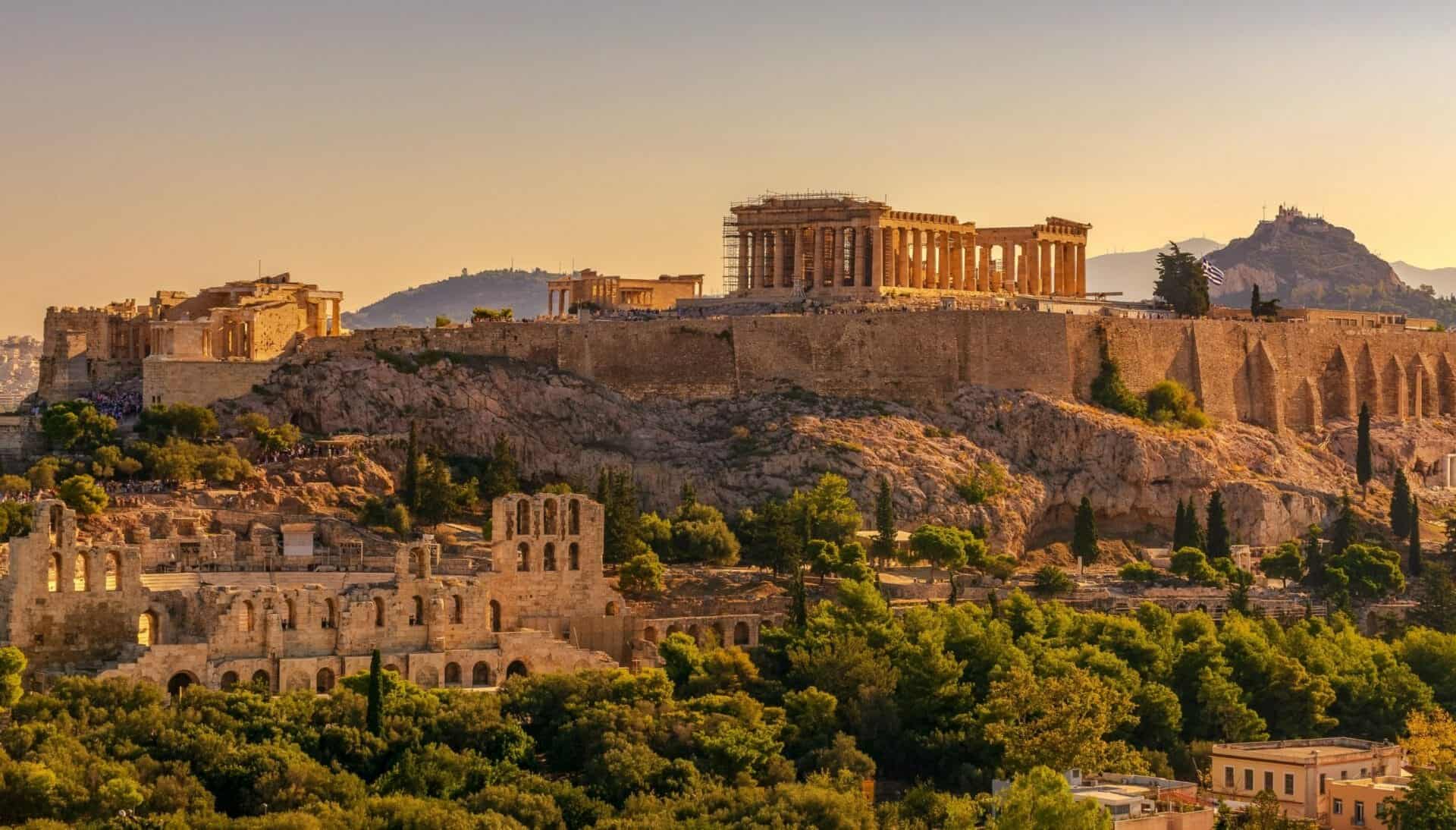
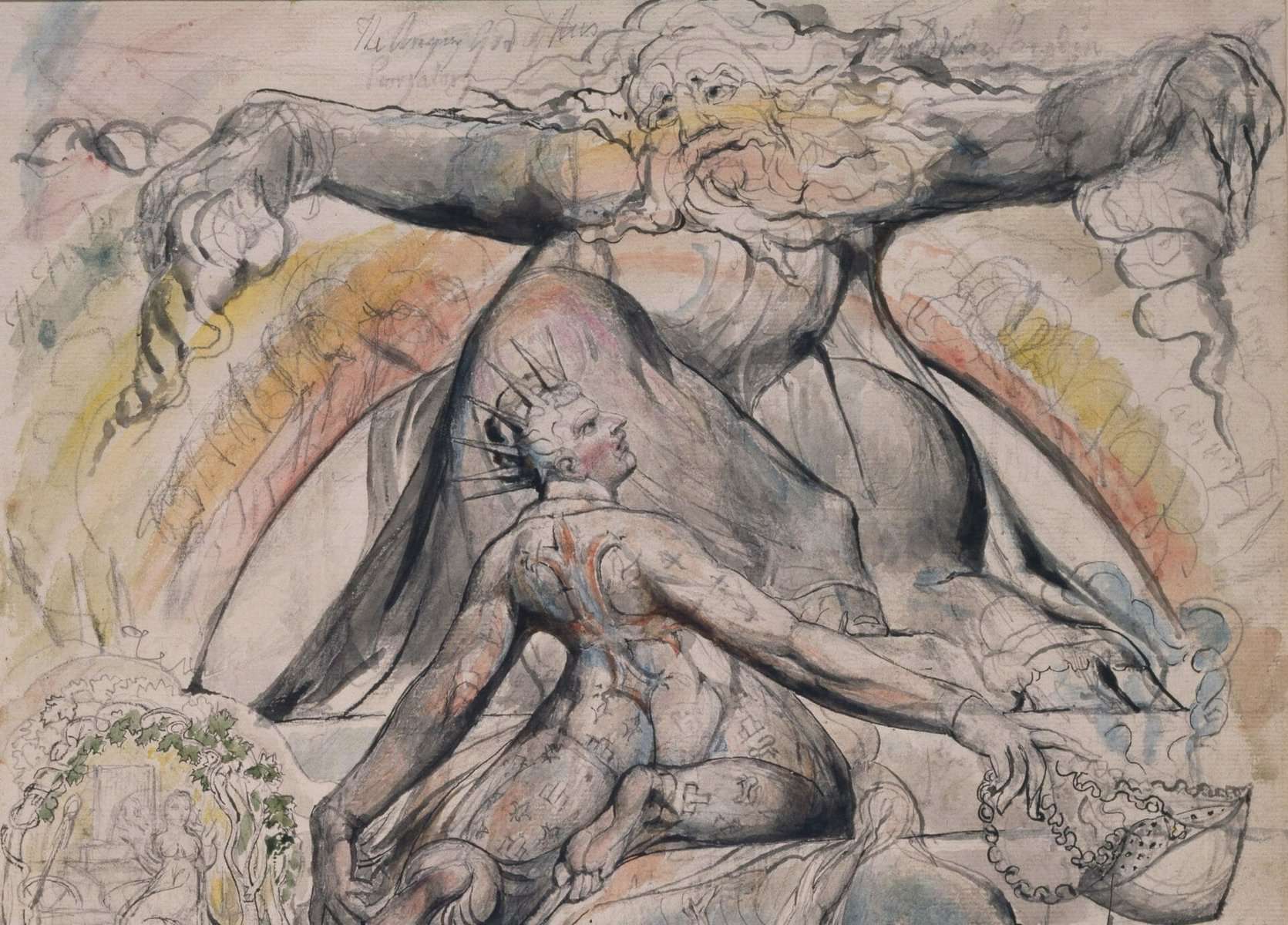
Emotion, nature and individualism are some of the key themes of Romanticism. This cultural movement became popular in Western Europe during the late eighteenth century and was expressed primarily through art and literature. However, the major intellectual movement which preceded Romanticism was the Enlightenment, during which philosophers emphasised rationalism in the pursuit of knowledge. Thus, Romanticism has often been posed as an opposite reaction to the Enlightenment.
Through using Gale Primary Sources, I have gained access to a number of notable works from the Romantic period, from paintings to poems, as well as the opportunity to explore how these works have been perceived since their initial creation. Primary sources highlight how Romanticism was a dynamic and varied movement. Romanticism responded not only to the Enlightenment, but the many political and social developments, such as revolution and industrialization, which had created a backdrop for the turn of the nineteenth century.